Can AI Replace Skilled Welders?
AI is taking over the world—well, not like in post-apocalyptic movies, where robots threaten humanity. Artificial Intelligence is used in various industries today, including welding.
Automated welding uses specialized equipment, welding robots, and software to produce welds with minimal human interaction. Robotic welders can produce quick, high-quality, repetitive welds, which are used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and general metal fabrication.
Robots gained popularity in large-scale mass manufacturing to improve efficiency and battle the shortage of skilled welders. Automated welding is improving, which raises a serious question: Can AI replace skilled welders? Stick to our article to learn more about the future of welding.

Robotic Automated Welding vs. Skilled Manual Welding
Source: https://robodk.com/blog/9-types-of-robot-welding/
Role of Welding Automation in Modern Welding
Welding automation involves using specialized equipment, welding robots, and advanced software to move, position, fixate, and weld two pieces with minimal operator intervention. With minimal interference, all equipment works in conjunction to increase the productivity, safety, speed, consistency, and quality of the weld.
Modern automation includes fully automated systems. Machines load, position, and unload parts, and robotic arms weld the pieces. However, there are collaborative robots, or cobots, that work alongside humans.
Automation systems vary in automation, flexibility, and scope of application. We are seeing fixed or hard automation that is ideal for mass production and simple, repetitive welding tasks. On the other hand, intelligent or flexible automation is highly customizable. You can reprogram and adjust the system to fit your needs.
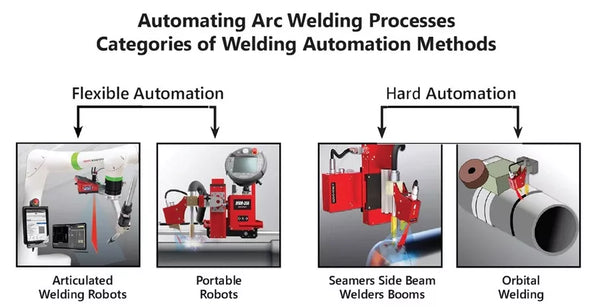
Methods of Welding Automation: Hard vs. Flexible Systems
Source: https://www.thefabricator.com
Rise of Automated Welding and AI
The advantages of automated welding systems include increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and the ability to produce repetitive, high-quality welds. These benefits make automated welding a suitable option for mass production and larger manufacturers. However, one of the leading causes of the increased use of welding automation is the welder shortage.

Automated Welding in Mass Production
Source: https://americantorchtip.com/blog/robotic-welding-and-automotive-manufacturing/
The American Welding Society (AWS) estimates a shortage of 330,000 skilled welders by 2028. The majority of welders today are between 55 and 60 years of age. Combined with the relative lack of young welders entering the profession, we could be facing a significant shortage of skilled welders in the future.
Large manufacturing companies dealt with the crisis by investing in welding automation. Although the initial investment in equipment and robots is high, their efficiency, high speed, low maintenance, and reduced labor costs eventually pay off.
The advantages, combined with the welder shortage, have led to a rise in automated welding and AI in welding. Welding automation started in automotive production, but today, it is seen in aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, and more.

Automated Welding and AI in Shipbuilding
Source: https://pemamek.com/welding-solutions/shipbuilding/
Advancements in Automated Welding and the Introduction of AI
New technologies and advancements in automated welding have made welding robots extremely precise and efficient. Improvements have enabled robots to work at high speeds and enhance the quality of the weld by providing real-time monitoring, adjustments, and learning.
Intelligent and adaptive welding systems have been constantly developed since the 2010s. AI, machine learning, and IoT are integrated into welding systems, allowing for predictive maintenance, adaptive welding, and remote monitoring.
Modern systems utilize AI to monitor weld quality in real-time and adjust parameters on the fly. Robots make adjustments based on material type, thickness, and joint configuration. Smart sensors monitor welding parameters such as voltage, amperage, arc length, or travel speed. If there are any abnormalities, the machine attempts to adapt or completely stops the process and notifies the operator.
Adding artificial Intelligence to the mix of automated welding enhances productivity and efficiency through optimized processes. It also improves quality control and reduces rework costs. By increasing quality and reducing rework, AI enhances competitiveness and profitability.

3 Development Stages in Arc Welding
Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2504-4494/8/1/22
Are AI and Automated Welding the Same?
While both processes, AI and automated welding, are performed by robots, they are fundamentally different. It can get pretty confusing, but here are the most notable differences.
Automated welding involves using robots and equipment that are preprogrammed to complete a single welding task. These robots do not make any decisions; they just follow the instructions. With the simplest robots, operators must observe the entire process. If the robot encounters abnormalities, it can stop or signal the error.

Automated welding uses robots for preprogrammed tasks.
Source: https://robodk.com/blog/10-tricks-for-robotic-welding/
Artificial Intelligence (AI) makes real-time decisions based on learning from experience and information. Once correctly configured and fed with information, AI algorithms evaluate historical data and optimize based on patterns. AI sensors can detect real-time abnormalities, adapt the parameters on the fly, or add suggestions that can further improve the quality or efficiency of the welding process.
AI systems often work in conjunction with regular robots to improve their efficiency and quality. However, adding intelligent sensors and machine learning can increase the overall costs of automation.

Integrate AI systems into robotic welding to enhance efficiency and weld quality.
Source: https://www.manufacturingtomorrow.com/
Can AI Completely Replace Skilled Welders?
As you can see, Artificial Intelligence can significantly improve the speed, efficiency, and quality of welding. Robots are getting better, but they cannot replace the human mind and judgment of a skilled welder.
It is still too early to expect fully automated AI systems to work without a human factor. AI-powered systems are perfect and often independent in high-volume production. However, with custom projects, tricky materials, and on-the-fly adjustments, human welders still hold the edge.

Manual Welding Custom Projects
Photo by @jamesharris910 (TikTok)
AI is indeed making everyday welding much faster and more convenient. However, skilled (human) welders will always be needed to make vital decisions on more complex and intricate projects. So, if you are afraid AI may take your job as a welder, be sure it will not happen anytime soon.
However, many large-scale manufacturers are switching to automation. That's why we will discuss the strengths and weaknesses of both and give you some tips on how to stay in the game, even if the rules change.

Audi Uses AI-Powered Automated Welding to Boost Efficiency
Source: https://www.audi-mediacenter.com/en/
AI Welders vs Manual Welders
Both automated (AI) welding and manual welding have their ups and downs. The final decision largely depends on factors such as precision, consistency, cost, flexibility, and skill requirements.
In a nutshell, automated welding is best suited for high-volume, consistent production in controlled environments. Meanwhile, manual welding remains essential for custom work, repairs, and tasks requiring adaptability and finesse.
AI-powered welding robots are leveling up as more information is available on the Internet. The more the machine learns, the better its judgment can be, but only to a certain point. Robots learn based on patterns, but once the situation throws them a curveball, they fail to react.
So, let's further discuss the strengths and weaknesses of automated and manual welding.

Robotic Welding vs. Manual Welding
Source: https://www.genesis-systems.com/blog/robotic-welding-vs-manual-welding-improving-quality-efficiency
Strengths of Robots and AI-powered Systems
-
Robots are fast and effective. Automated welding offers unmatched speed compared to manual welding. In repetitive mass production, robotic welding systems crank out thousands of spot welds daily, keeping production lines moving. Besides periodic maintenance, robots don't have downtime. They don't need to rest like humans, so uptime combined with speed provides significantly higher efficiency compared to manual welding.

Robotic Welding in Repetitive Mass Production
Source: https://www.evsint.com/collaborative-robot-vs-industrial-robotwelding-robot/
-
Automated welding produces consistent, precise, and repetitive welds. Unlike humans, robotic welders are not affected by fatigue, stress, or distractions. Robots don't care if it is a Monday morning, and they certainly didn't spend a night drinking with friends. Combined with AI-powered systems, robots can produce extremely repetitive, consistent, precise, and high-quality welds every time. Consistency is particularly noticeable when you need to complete thousands of parts a day, and one bad weld can ruin the production.
-
Robotic welders do all the dirty work, keeping operators much safer. Welding involves working around high heat, the intense radiation of the arc, fumes, and sparks. Automated welding features various protection systems that keep operators out of harm's way. Robots handle high-heat, high-risk environments without the need for high-safety protection equipment.

Robotic Welding Process
Source: https://kawasakirobotics.com/blog/integration-insights-for-welding-applications/
-
Automated systems provide high ROI. The typical ROI of robotic systems is 1 to 3 years. The high quality and repeatability of the welds significantly reduce the need for costly rework. Producing high-quality welds each time minimizes material waste. Combined with increased speed, efficiency, and reduced labor costs, automated welding quickly pays off.
-
AI systems detect and react. AI algorithms evaluate historical data and optimize based on patterns. They can respond and adapt to abnormalities to improve the quality of the weld and minimize the rework. Modern systems can learn, suggest improvements, or troubleshoot issues.

AI-Powered Robotic Welding System with Real-Time Monitoring and Adaptive Control
Photo credit: DELMIA
Weaknesses of Robotic Welders
Although robotic welding systems are getting better, they still show some weaknesses. Here are the most notable drawbacks compared to manual welding:
-
Automation systems and all equipment, including robotic arms, power supplies, software, fixtures, and sensors, are initially expensive. Even entry-level robotic systems can hit six figures, and without properly trained operators, they can be practically useless. Small to medium companies can take years to recover the invested money. Meanwhile, hiring a skilled welder will rarely cost more than six figures a year.

Framework of a Typical Welding Robot System
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/
-
AI systems are still not perfect. Although artificial intelligence learns and adapts, it is still bad at improvising. If the conditions drastically change, robots can't make judgment calls like human welders. Robots still lack the real-time decision-making and creativity of humans.
-
Limited flexibility and adaptation. Robots are perfect for repetitive welds, but if the conditions change, they can struggle. Introducing a new material or new welding process requires complete reprogramming. The entire process can be time-consuming and create downtime. Meanwhile, manual welders can just grab the different sets of equipment and start TIG welding instead of MIG welding or switch from steel to aluminum in no time.

4 Main Manual Welding Processes
-
Downtime can stop the entire production. Minor glitches, bugs, or malfunctions can also cause downtime. Even the most minor bugs in the software can bounce the robots off track and lock up production lines until an engineer fixes them. Avoiding bugs requires regular maintenance, which can be expensive, and that's why some smaller businesses skip it. Meanwhile, troubleshooting and repairing a single manual welder is much faster.
-
It is difficult to scale down. Most robotic welding systems are designed for grind mode and high-volume production, so scaling them down to custom or low-volume jobs can be ineffective. The exceptions are small, desktop robotic systems, but you cannot scale them up.

Robotic Welding Systems in High-Volume Production
Source: https://www.robots.com/articles/manufacturing-window-frames-with-robotic-welding
Strengths of Skilled Welders
-
Flexibility: Unlike machines, human welders can adapt to complex geometries, custom jobs, and varied materials on the fly. One welder can perform several welding methods on various material types, allowing it to adapt to the given situation without reprogramming or downtime.
-
Lower Upfront Cost: No need for expensive machinery—just skilled labor and basic tools. Most straightforward robotic systems often cost six figures, while skilled welders cost roughly that much money for a year.
-
Human Judgment & Skill: Human welders are capable of recognizing and adjusting to irregularities during the welding process. Although some advanced AI machines can do the same, they can't make judgment calls. Humans possess real-time decision-making and creativity that can help them problem-solve, troubleshoot, and diagnose issues.

Repairing an Aluminum Fuel Cell with TIG Welding
Photo by @jakewoodard (TikTok)
-
Better for custom and complex work. AI robots follow programmed paths, but custom projects often require adjustments mid-weld. Humans can make real-time corrections, innovate, or fine-tune a design. Some super-complex work, like artistic welds, simply cannot be coded.
-
Welding robots still cannot work without a human factor. Although robots are replacing manual welders, they still cannot work independently. Robots still need a babysitter to monitor their work, start or stop the process, and program their path.
-
Suitable for on-field work and repairs. If something breaks on the field, you cannot take a robot to deal with it. Robots can pre-weld replacement parts, but you need human welders to install them or repair the damage.

Repair Cracked TIG Welds
Photo by @liftarcstudios (TikTok)
Weaknesses of Skilled Welders
-
They can be inconsistent. Fatigue, mood, and real-life events can cause human errors. These errors can affect the quality of the weld, eventually requiring rework, which takes time and causes material waste and additional costs.
-
Workforce shortage. Skilled welders are hard to come by. As noted above, most skilled welders are old, while the number of new welders is decreasing. Skilled welders often demand higher wages, and training new welders can take a long time, even though there are many shorter courses. Still, getting enough experience for specific tasks takes time, so some manufacturers are taking shortcuts by automating the process.

Skilled Welders Training New Welders
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zkjeX1s1yGI
-
Slower production rates. Manual welders cannot match the pace of robots, especially on repetitive, mass-production parts. Robots can output enormous amounts of parts daily without feeling sore or tired the next day. Of course, that's the case as long as we are talking about simple designs.
-
Safety concerns. Working with high heat, radiation, and fumes increases the risk of injuries from heat, fumes, and repetitive strain. Long-term exposure can have terrible consequences or even cause chronic illnesses. Injured welders cannot work, reducing overall productivity and efficiency.

How to Stay in the Game?
AI systems and automated welding should be your friend, not your enemy. If you are feeling like you might lose a job to a machine, there are several things you can do to make sure you keep up with the game. Here are some practical tips.

Automated Robotic Welding
Source: https://www.canadianmetalworking.com/
Keep Up with the Changes
Don't limit yourself to manual welding and knowledge. Be ready to learn and embrace welding automation. New titles like "welding automation specialist" or "welding robot operator" are popping up daily. As a skilled welder, you can complete the robotic operator training and improve your knowledge.
Certification means you are safe and fit for hybrid roles as both a manual welder and a welding robot operator. Welders who can read digital blueprints, analyze real-time welding data, and optimize robotic systems will be in super high demand.

Robotic Operator Training
Source: https://adaptecsolutions.com/services/fanuc-robotics/fanuc-robotic-training/
Embrace the AI
As noted, AI and automated welding are not your enemies. They are there to help you boost the production and quality of the welds, but they cannot work independently.
AI systems can analyze welds in real time, spot inconsistencies, and tweak parameters, but they need welders to guide and fine-tune them. Without human oversight, robots are just expensive toys, so use that to your advantage.
Humans and Robots Working Together
Modern automation often uses collaborative welding robots or cobots to get the best of both worlds. These machines are designed to work alongside humans, profiting from the benefits of both.
You get the precision and consistency of robots combined with human intuition and judgment. Working back-to-back with robots benefits everyone, so be ready to approve it.

Collaborative Welding Robots Working with Human Operators
Source: https://blog.hirebotics.com/4-reasons-consider-welding-cobots
Adapt to Industry 4.0 and IoT
Smart factories and production lines are the new "meta" in industry, including welding. These factories include a series of systems and sensors that monitor, analyze, and upload welding data.
Companies that use these tools and sensors are ready to improve the process and invest in quality. You, as an operator, should be able to understand the patterns and data and make adjustments that can make the process more efficient and better.
Predictive Maintenance
The good thing about AI robotic systems is that they feature predictive maintenance systems. These protective systems analyze real-time data to spot wear and tear and recommend maintenance before larger accidents occur.
Welders who embrace these systems invest in productivity. Scheduling maintenance or repair before serious breaks or bugs significantly reduces downtime. Scheduled maintenance allows people to plan outages and work around them, keeping the line moving as soon as possible.

AI and Predictive Maintenance in a Modern Factory
Photo credit: Tangent Works
Final Thoughts
Automated and manual welding each offer unique advantages suited to different applications. Automated welding excels in high-volume, repetitive tasks, providing consistent quality, speed, and long-term cost savings, especially in industrial production settings.
However, it lacks flexibility and requires a high initial investment and technical expertise. In contrast, manual welding offers adaptability, precision in complex or custom jobs, and lower startup costs, but it is slower, more variable, and labor-intensive.
Ultimately, the best approach depends on the project's specific needs. Many operations benefit from integrating both methods to balance efficiency with craftsmanship and adaptability.
🧐Can AI Replace Skilled Welders? FAQ
1. What are the advantages of automated welding compared to manual welding?
2. Can AI completely replace skilled welders?








Leave a comment